The European Union requires manufacturers to introduce a range of safety improvements on all new cars to protect pedestrians in the event of a collision with a car. Jaguar and Mercedes-Benz are the first to introduce new cars with features that comply with these standards. In Japan, Honda has developed the world’s first motorcycle airbag.

Jaguar’s all-new XK sports car, which goes on sale in early 2006, features the Pyrotechnic Pedestrian Deployable Bonnet System. This advanced sensing system can distinguish between different types of frontal impacts. Then in the case of a pedestrian impact, the hood automatically ‘pops’ up a few inches to create a cushioning effect between the engine and the hood. This helps to isolate the pedestrian from hard components in the engine compartment. This all happens in less than a tenth of the time it takes to blink an eye, 30 milliseconds, using forces up to 50 times the force of gravity to lift the 50-pound hood.
The advanced sensing system, mounted in the front bumper, can discriminate between a pedestrian collision and any other possible front-end collisions. The Jaguar system normally operates at vehicle speeds where it provides the most benefit and is automatically disabled outside of this speed range. It is completely separate from any other crash protection system on the vehicle including airbags. The new XK also has a passive bumper system to reduce leg injury through the use of crushable foam and plastic covering.
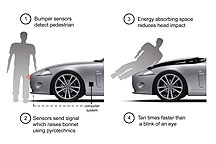
Mercedes-Benz, a long time pioneer in technology to protect pedestrians, has taken a more passive approach to solving the same problem. The underside of the hood on the new S-Class sedan has been designed for programmed deformation and impact-energy absorption in a collision with a pedestrian. A "yielding" hinge supports the deformation of the hood and also helps to reduce injuries to pedestrians as well as bicyclists and motorcyclists. The front fenders are attached to the upper longitudinal members by a special fixing element with precisely calculated rigidity characteristics. It is programmed to give way in the event of an impact.
The deformation space between the hood and the engine components beneath it - an important factor in accidents where there is contact between the pedestrian's head and the bonnet - has been increased in two ways. First, the front section is some 22 millimeters higher than in the previous model. Secondly, the engine, shock-absorber towers, reservoirs and control gear have been located up to 13 millimeters lower. The Mercedes engineers have also reduced the overall height of the windscreen-wiper system, thereby increasing the deformation space. The front bumper has a flush, foam-filled spoiler edge to ensure early and even support in a collision.
Honda has developed the world’s first production motorcycle airbag system and will offer it on the new Gold Wing motorcycle scheduled go on sale in late spring 2006. The new system can help lessen the severity of injuries caused by frontal collisions.

The Motorcycle Airbag System’s airbag module, containing the airbag and inflator, is located in front of the rider. The airbag inflator receives an electronic signal transmitted by the airbag ECU (electronic control unit) instructing it to release nitrogen gas to inflate the airbag. Four crash sensors attached on both sides of the front fork, two on either side, detect changes in acceleration during frontal impacts. The ECU performs calculations, comparing this data to standard motorcycle behavior, to instantly determine when a collision is occurring and whether or not it is necessary to inflate the airbag. Inflating rapidly after the impact, the airbag can absorb some of the forward energy of the rider, reducing the velocity at which the rider may be thrown from the motorcycle and helping lessen the severity of injuries caused by the rider colliding with another vehicle or with the road.




